a. Energy use in the United States and the World
- by type of energy
- by use or sector of the economy
- see wiki pages below
b. Geological reserves
- mining of minerals and energy sources have damaging impacts on the Earth
- mineral resources
- metals such as aluminum, copper and iron
- resources are limited
- can change the depletion time by recycling
- prices can drive depletion
- energy such as coal
- energy is not recyclable <-- this is a key point
- "recycling" metals is very different process than trying to find "renewable" energy
- amount of reserves
depends on the certainty of knowing that it exists and the economics of extraction (i.e. mining)
| |
undiscovered |
discovered |
|
low
cost |
other
resources |
RESERVES |
economical |
higher
cost |
other
resources |
other
resources |
non-
economical |
| |
deceasing
certainty |
known |
|
c. Non-renewable energy - such as fossil fuels
- Fossil fuels
- came from buried plant, algae and other biomass put under pressure for a long time
- oil or coal reserves
- known reserves
- predicted reserves
- detection
- change in methods or cost allow more reserves to be cost-effect
- unknown and uncertain
d. Depletion of fossil fuel reserves
- depends on
- amount available
- use rate and cost
- increase in use
- economic growth
- population growth
- Hubbert "bubble" - see the simulation
e. Comparison of non-renewable energy sources
- advantages and disadvantages of:
- (the potential damage from these sources)
- oil
- natural gas
- coal
- nuclear
- nuclear fuel cycle, not just plant operation
f. Impact of fossil fuels
We hear a lot about global warming or global climate change but there are other impacts
- global climate change - estimated impacts of business as usual
- warming
- extreme weather (hurricanes and droughts)
- flooding
- sea level rise
- other environmental impacts
- pollution from combustion furnaces and engines
- mercury from coal
- urban pollution from cars
- risks from fossil fuels
- oil spills
- oil well leaks and fires
- inter-nation strife
g. Net energy - the only energy that really counts
"net energy" is what counts
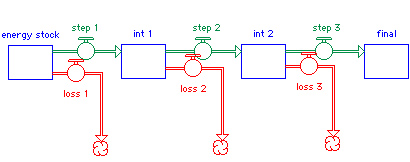
| 85% x |
85% = |
|
72% |
| 80% x |
80% x |
80% = |
51% |
| 70% x |
70% x |
70% = |
34% |
| 30% x |
30% x |
30% = |
2.7 % |
h. preview of next lecture
- renewable energy sources and impacts
- energy efficiency
- life-cycle analysis and embedded energy in the structures
- looking for total quality of life and genuine progress, not just economic gain


![]()