Introductory comments
- assignments for the week - check the lab schedule carefully
- Crux question - reminder on the purpose
- bring together approach for the week and the env sci examples
- this week - stock and flow systems with food chain or nutrient cycles
Themes for this week
Models are simplifications of the real world that allow us to focus on particular aspects.
In this case we will focus on stocks and flows of material and/or energy.
We will simplify greatly, allowing us to use only a few building blocks to create descriptions of a wide range of examples. This allows us to see the structural similarities between disparate systems.
We will be looking for 5 major motifs or recurring structures:
- open and closed systems
- stock limitation
- steady state
- positive feedback
- negative feedback
You will also see how to tie sub-models for different stuff together.
This lecture:
- examples
- setting up stock and flow descriptions
- food chain, food web, food web with recycling
- energy is an open system, material may be closed
- recycling
- ecological
- mineral
- Four motifs
- Coupled models - combing sub-models through information links and constraints
1. Range of examples we will explore in lecture, text, and other resources
- metabolism of a single organism
- short food chain from autotroph to herbivore to carnivore
- food web
- food web with recycling
- aluminum recycling
- biogeochemical cycles of carbon and nitrogen
- population growth
- coupled models:
- population and wealth relationships
- population growth and collapse
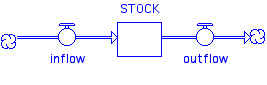
2. Stock and Flow Systems Approach
sometimes just called "systems"
icons
rules:
any connected stock and flow can only contain one type of stuff (energy or material) - for example in can only have energy or nitrogen
set boundaries of the system
determine major stocks and flows
model with information flow
3. This approach is often used in ecology for studies of energy and material flow
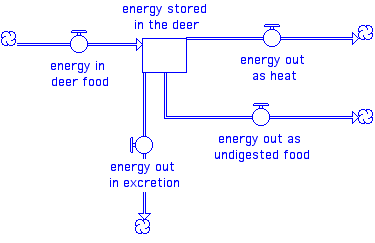
individual organism metabolism
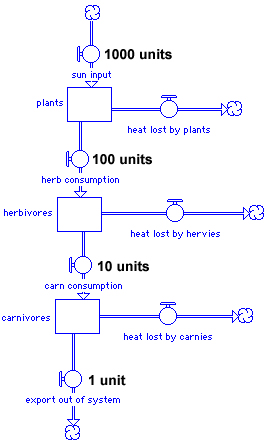
food chain from lower trophic levels to higher
Trophic levels
- primary producers (plants)
- herbivores (consume plants)
- carnivores (consume herbivores)
- 2nd carnivores (consume other carnivores)
- -----
- mixed level, omnivores
- detritivores and recycling (consume dead stuff)
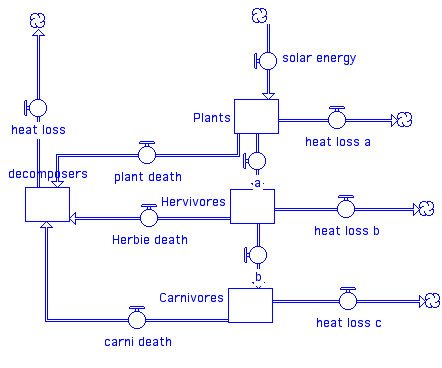
This model illustrates the loss of energy at each step and is often called the energy pyramid
|
 |
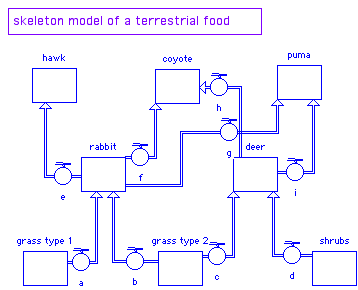
Food webs (with multiple interacting components within one trophic level)
depictions of these
systems model of multiple trophic levels
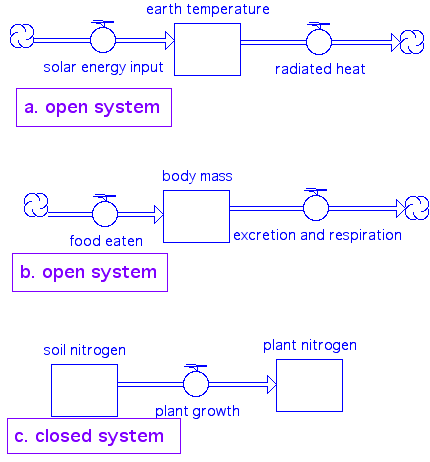
4. Open and Closed Systems
It's up to you to describe where the boundaries are
Some times this is arbitrary
Sometimes there are reasons
- city or state boundary
- watershed
- island or continent
- geographical region, such as high desert
- biogeographical region, such as a biome or eco-region
Sometimes it has to be that way
- energy in an ecosystem is open
- material flow can be closed
|
 |
5. Recycling in eco-systems
5a. autotroph, herbivore, carnivore, detritivore+bacteria
following nitrogen - which goes between organic and inorganic forms of N
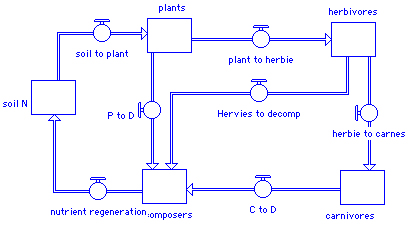
The energy diagram of this would not be closed
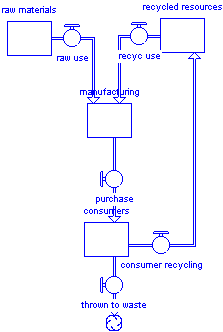
5b. Material loss in industrical recycling
because processes have loss
some stock in the recyling has to be replaced with Al ore
but ... lower energy costs for recycling drove mre uses of Al and more consumption of the ore (see this next term in more detail)
|
 |
6. Four motifs for regulation
Stock Control - when the reservoir is empty then flow stops
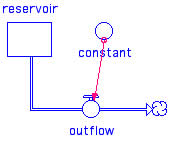
Steady State - when inflow equals outflow, stock stays the same
Positive Feedback

Negative Feedback

7. Combining models of related flows
This is necessary because only one type of stuff can be in the stocks and flows.
Forces you to think about that and be clear.
People and Wealth
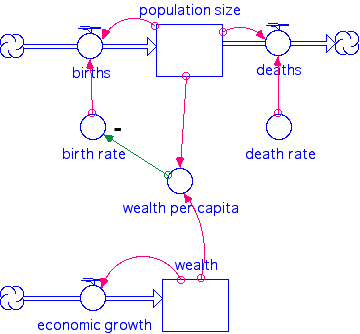
People and consumption of recycled material - Hubbert Model for Peak Consumption

8. Summary
|


![]()