What is a wetland?
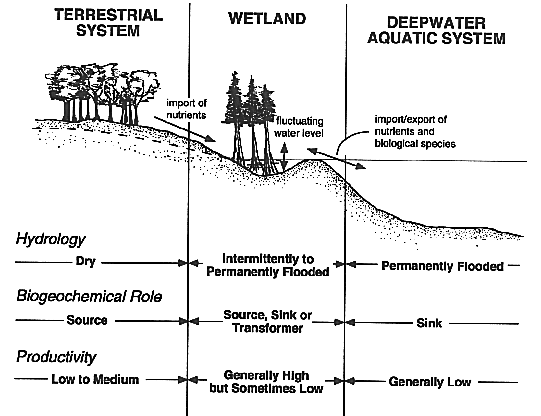
Wetland Profile - Transition
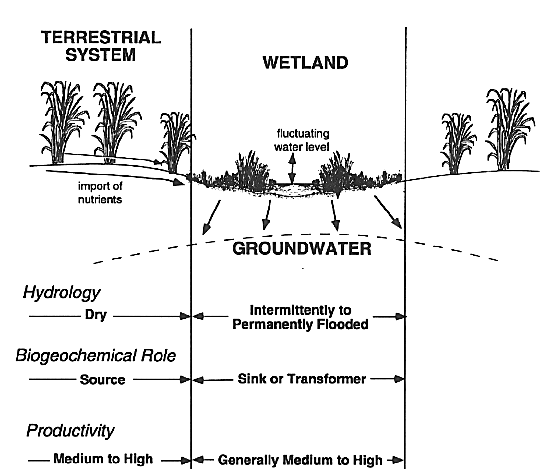
Wetland Profile - Depression
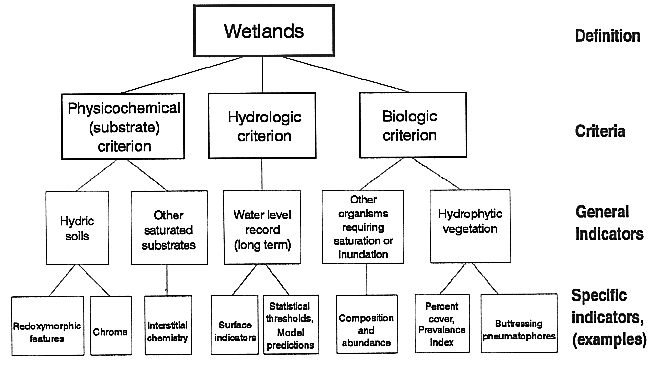
Reference Definiton
Definition Diagram
Wetland types
USFWS Classification System
Wetland soils
Whiteboard
1975: US Army Corps of Engineers - proposed definition · regular inundation by tidal, riverine or lacustrine flowage · inland and coastal shallows, marshes, mudflats, estuaries, swamps
1976: US Fish and Wildlife Service - interim classification · excess water is the dominant factor determining soil/plants/animals · water table at or near surface long enough to promote formation of hydric soils/ support hydrophytes
1977: US Army Corps of Engineers - definition · inundated or saturated by surface or ground water at frequency/duration sufficient to support vegetation adapted to saturated soil conditions · marsh, swamps, bogs
1979: US Fish and Wildlife Service - classification · transitional areas between terrestrial and aquatic systems, water table at or near surface, have one or more of following attributes: · support predominantly hydrophytes · predominantly undrained hydric soil · saturated or covered by shallow water some time during growing season
1985: Food Security Act · predominantly hydric soil · support predominantly hydrophytic vegetation

COASTAL WETLAND ECOSYSTEMS
· Tidal Salt Marshes
· Tidal Freshwater Marshes
· Mangrove Wetlands
INLAND WETLAND ECOSYSTEMS
· Inland Freshwater Marshes
· Northern Peatlands
· Southern Deepwater Swamps
· Riparian Wetlands Return to Week 1 - Lecture 1
Return to overhead index
Hydric Soil - defined by US Soil Conservation Service A soil that is saturated, flooded or ponded long enough in the growing season to develop anaerobic conditions in its upper part. Organic Soils (Histosols) - > 20-35% organic material · Saprists (muck) >2/3 decomposed material, < 1/3 plant fibers · Fibrists (peat) <1/3 decomposed material, > 2/3 plant fibers · Hemists (muck/peat) conditions between saprists & fibrists Mineral Soils - < 20-35% organic material · Gleyed - semipermanently or permanently flooded · Mottled - seasonally flooded Gley/Mottle Formation Depend On: · Presence of sustained anaerobic conditions · Sufficient soil temperature · Presence of organic material U.S. Army Corps Delineation Manual - field indictors · Chroma - 1 with or without mottles · Chroma - 2 with mottles
