Chemistry 332 - Spring 1996
Elements of Organic Chemistry II

Professor Carl C. Wamser

FINAL EXAM, Part 2
Answer Key
June 13, 1996
1. (20 points) During digestion, larger molecules are broken down to smaller
ones, as described below. Identify by name (structure optional) the specific
lettered compounds referred to in the scheme below.
table sugar (sucrose) --> A + B --> C + D --> E -->
F
starches --> A --> B --> C + D --> E --> F
fats --> G + H ( G --> D --> E --> F ) ( H -->
E --> F )
Some compounds may have phosphate attached, but we will be ignoring that,
e.g., glycerol-1,3-diphosphate should just be called glycerol.
Hints:
A and B are C6 compounds
C, D, and G are C3 compounds
E is a C2 compound
F is a C1 compound
Compound D is a D-sugar.
Compound E contains sulfur.
A = glucose
B = fructose
C = dihydroxyacetone
D = glyceraldehyde
E = acetyl coA
F = carbon dioxide
G = glycerol
H = fatty acids
Identify which process represents the citric acid cycle (or Krebs cycle).
E --> F
Identify glycolysis in the scheme above.
A --> B --> C + D --> E
2. (15 points) Select one of the base-catalyzed reactions below and write
a complete mechanism. Show all intermediates and all resonance forms.
(Hint: base-catalyzed mechanisms involve negatively charged intermediates.)
a) aldol condensation of acetaldehyde

b) Claisen condensation of ethyl acetate

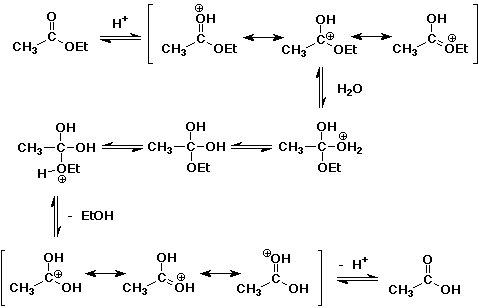
3. (15 points) Select one of the acid-catalyzed reactions below and write
a complete mechanism. Show all intermediates and all resonance forms.
(Hint: acid-catalyzed mechanisms involve positively charged intermediates.)
a) bromination of cyclohexanone

b) hydrolysis of ethyl acetate