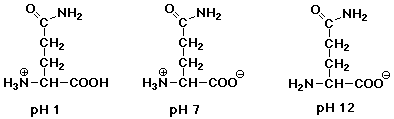Chemistry 332 - Spring 1996
Elements of Organic Chemistry II

Professor Carl C. Wamser

EXAM 3 - Answer Key
June 4, 1996
1. (15 points) Write accurate structures for the following:
a) N,N-dimethylglycine (at pH 7)

b) the triglyceride of butanoic acid (glyceryl tributanoate)

c) the enol tautomer of cytosine

d) tryptophanylaspartic acid (at pH 7)

e) deoxythymidine 5'-phosphate

2. (12 points) For each of the molecules below, indicate what structures
would predominate in aqueous solutions of pH 1, pH 7, and pH 12.
a) glutamine
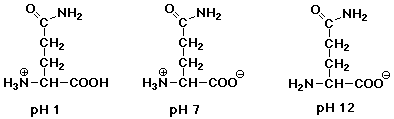
b) lysine

3. (16 points) Using the side chains of specific amino acid residues,
illustrate each of the different types of interactions that might contribute
to a protein tertiary structure at pH 7.
Example: disulfide linkage Cys - - Cys )-CH2-S-S-CH2-(
*(All of the answers below have multiple possibilities.)*
a) charge-charge (Coulombic) attraction

b) charge-dipole H-bonding

c) dipole-dipole H-bonding

d) nonpolar (hydrophobic) interactions

4. (12 points) Examine the trends in pKa data for the three amino acids
shown below, representing typical alpha- , beta- , and gamma-aminoacids.
pKa values for:
glycine H2N-CH2-COOH 2.34 9.60
beta-alanine H2N-CH2-CH2-COOH 3.55 10.24
4-aminobutanoic acid H2N-CH2-CH2-CH2-COOH 4.03 10.56
(3 pts) Are the carboxylic acids in the natural alpha-aminoacids more or
less acidic than the carboxylic acids in beta- or gamma-aminoacids?
More acidic
(3 pts) Are the amine groups in the natural alpha-aminoacids more or less
basic than the amines in beta- or gamma-aminoacids?
Less basic
(6 pts) Explain the differences.
The carboxyl groups have a nearby NH3+, which acts as an electron-withdrawing
group and makes it easier to lose a proton from COOH. The closer the NH3+
group, the stronger the acid.
The ammonium ions have a nearby COO- group, which acts as an electron-withdrawing
group (the polar C=O bond), and makes it easier to lose a proton from NH3+.
The closer the COO- group, the stronger the NH3+ acid (which means the
amine base is weaker).
5a. (5 points) Illustrate why arginine is so basic by showing the protonated
form of the guanidine side chain in all of its resonance forms.

5b. (2 points) Predict which N in guanine is most basic.
(This is related to the question above.)

The indicated N resembles that in the guanidine group above (i.e., a C=N
surrounded by two other N atoms).
6. (18 points) The informational strand of a DNA contains the base sequence
shown below (written in the standard 5' to 3' direction).
C G T T A C C T A C A A G C C T G T
a) (3 pts) Indicate the base sequence that would match this in its complementary
strand
G C A A T G G A T G T T C G G A C A (in 3' to 5' direction)
b) (3 pts) Indicate the base sequence in the m-RNA that would be transcribed
C G U U A C C U A C A A G C C U G U (in 5' to 3' direction)
c) (6 pts) When the message is translated into peptide synthesis, describe
each of the tRNAs that would be called for, in terms of their anticodons
and the aminoacids they would bring in
anticodons written in 3' to 5' direction:
GCA - Arg
AUG - Tyr
GUA - Leu
GUU - Gln
CGG - Ala
ACA - Cys
d) (6 pts) There are 6 C bases in the original DNA sequence written above.
Number them 1 to 6. A mutation of C to T would cause drastic changes in
just two cases, a minor change in one case, and have no effect in three
cases. Indicate by number which C bases would cause these effects.
C1 G T T A C2 C3 T A C4
A A G C5 C6 T G T
i) drastic changes
C1 : CGU to UGU changes Arg to Cys
C4 : CAA to UAA changes Gln to Stop
ii) minor change
C5 : GCC to GUC changes Ala to Val
iii) no effect
C2 : UAC to UAU are both Tyr
C3 : CUA to UUA are both Leu
C6 : GCC to GCU are both Ala
7. (20 points) You have undertaken a project to find out everything possible
about the dipeptide PheLeu.
a) (3 pts) What is its RNA code?
One possibility is UUUUUA.
However Phe could be UUU or UUC
and Leu could be UUA or UUG or CUX (where X is any base)
b) (3 pts) Predict its isoelectric point.
5.75 (average of 9.13 and 2.36)
The N-terminus should be like Phe (pKa 9.13) and the C-terminus should be
like Leu (pKa 2.36). The isoelectric point is the midpoint between those
two (the only two places that could ionize on the dipeptide).
c) (8 pts) Predict the products that would result from treatment with
i) boiling concentrated HCl
Phe + Leu
ii) Edman's reagent
phenylthiohydantoin derivative of Phe + Leu
iii) trypsin
no reaction (or very slow reaction)
iv) chymotrypsin
Phe + Leu
d) (6 pts) Devise a synthesis using BOC as a protecting agent and DCC
as a coupling agent.
Phe --(BOC)--> BOC-Phe --(DCC)--> --(Leu)--> BOC-Phe-Leu
--(TFA)--> Phe-Leu