Chemistry 331 - Winter 1996
Elements of Organic Chemistry I

Professor Carl C. Wamser

Chapter 1 - Structure and Bonding
Tues, Jan 9
Why organic chemistry?
- carbon has unique chemistry
- bonds to every other element
- bonds to itself in long chains
- organic chemistry involves enormous variety
- many possible structures
- many possible reactions
Why learn organic chem?
- what do organic chemists do?
- understanding structures, reactions
- correlation of structures with properties
- synthesis of compounds with specific properties
- who else needs organic?
- basis of all life processes
- the great variety of structures and reactions make life possible
How to handle variety
- nomenclature
- clear methods for naming structures and reactions
- structures
- organized by functional groups
- reactions
- organized by reaction types (what happens?)
- organized by reaction mechanisms (how does it happen?)
What should you get out of organic?
- from complex names, be able to derive a structure
- from complex structures, be able to identify functional groups, predict
characteristic properties
- work through reaction mechanisms - what is a molecule likely to do under
certain conditions
- "think like a molecule"
A reaction example
- CH3OH + HCl --> CH3Cl + H2O
- Reaction type ?
- acid/base, oxidation/reduction, addition/elimination, substitution,
rearrangement
- substitution - of Cl for OH (identify bonds broken and made)
- Reaction mechanism ?
- how does the reaction occur (step-by-step)
A reaction mechanism
- Break the molecules into atoms
- Reassemble into products
- What's wrong with this mechanism?
- It would take too much energy (unnecessarily)
A better mechanism
- Balance bond breaking with bond making
- First an acid-base reaction:
CH3OH + HCl --> CH3OH2+ + Cl-
- Then a substitution:
CH3OH2+ + Cl- --> CH3Cl + H2O
The Periodic Table
- atomic number (defines element)
- atomic weight (isotopes)
- electron shells (rows)
- groups (similar properties)
- filled shells (the noble gases)
- valence electrons (for bonding)
Lewis Structures
- the octet rule
- atoms strive to get 8 electrons (full shell)
- ionic bonding
- gaining or losing electrons
- stabilized by Coulombic attractions
- covalent bonding
- sharing electrons
- most common bonding in organic compounds
Atomic Orbitals
- wavefunctions
- describe location of electrons
- s orbital (spherical)
- p orbitals (three: x,y,z)
- (dumbbell shape - 2 lobes)
- d orbitals (4 lobes)
- not usually needed for organic chemistry
- hybrid orbitals
- combination orbitals
Hybrid Orbitals
- sp hybrids (one s plus one p)
- makes two identical orbitals (linear)
- sp2 hybrids (one s plus two p)
- makes three identical orbitals (trigonal)
- sp3 hybrids (one s plus three p)
- makes four identical orbitals (tetrahedral)
Bonding
- attraction between negative electrons and positive nuclei
- repulsions between electrons
- repulsions between nuclei
- bonding is a balance between the attractions and repulsions
- characteristic bond lengths and strengths
Molecular Orbitals
- overlap of atomic orbitals
- electrons are close to two nuclei
- bonding and antibonding combinations
Sigma Bonds
- cylindrical symmetry
- formed by end-on overlap
Pi Bonds
- nodal plane through bond axis
- formed by side-on overlap
Writing Organic Structures
- Lewis structures
- all electrons shown
- Kekule structures
- show bonds as lines
- lone pairs sometimes omitted
- line structures
- omit lone pairs
- omit hydrogens on carbons
- omit carbons
(assumed to be at the end of every bond)
3-Dimensional Structures
- dotted-line / wedge
- ball-and-stick
- space-filling
Visualizing chemical structures
- Name (common or systematic)
- Condensed Formula (as usually typed out)
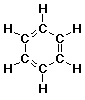
- Lewis Structure (all atoms and bonds shown)
- Line Structure (omit hydrogens, assume carbons at vertices)
- 3-D Structure (show bond orientations)
- Ball-and-Stick Structure (like a molecular model you could make)
- Space-Filling Model (approximates full size of electron distribution)
methane: CH4 
benzene: C6H6 
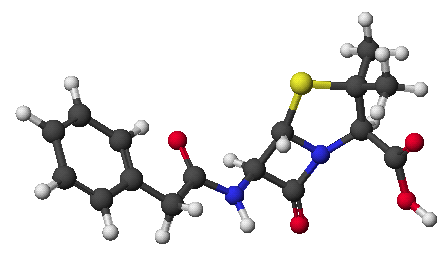
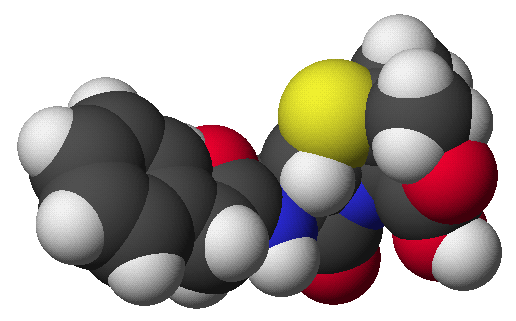
penicillin: 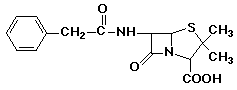
Try a 3-D image:
1) Click at the bottom after you read these instructions
2) Cross your eyes to see two double images
3) Make the middle images merge
Try it!
Thurs, Jan 11
Typical Valence
- H 1 valence electron 1 bond
- C 4 valence electrons 4 bonds
- N 5 valence electrons 3 bonds + 1 lone pair
- O 6 valence electrons 2 bonds + 2 lone pairs
- F 7 valence electrons 1 bond + 3 lone pairs
Molecular Orbitals
- H + H ---> H-H
- s + s ---> sigma bond
- H-H bond length 0.74 Å
- H-H bond strength 104 kcal/mole
Methane
- C + 4 H ---> CH4
- sp3 + s ---> four sigma bonds
- C-H bond length 1.10 Å
- C-H bond strength 104 kcal/mole
- orientation - tetrahedral
- bond angles 109.5°
Why Hybrid Orbitals?
- good shape (directional)
- allows high overlap in bonding
- maximizes electron density between atoms
- good orientation
- minimizes repulsions between orbitals
Ethane
- CH3CH3
- includes a C-C sigma bond
- overlap of sp3 - sp3 orbitals
- C-C bond length 1.54 Å
- C-C bond strength 88 kcal/mole
- C-H bond length 1.10 Å
- C-H bond strength 98 kcal/mole
- orientation - two tetrahedra
Ethylene
- CH2=CH2
- includes a C=C double bond (alkene family)
- overlap of sp2 - sp2 orbitals (sigma bond)
- overlap of p - p orbitals (pi bond)
- C-C bond length 1.33 Å
- C-C bond strength 152 kcal/mole
- C-H bond length 1.08 Å
- C-H bond strength 103 kcal/mole
- orientation - planar
- bond angles 120°
Acetylene
- HC=CH
- includes a C=C triple bond (alkyne family)
- overlap of sp - sp orbitals (sigma bond)
- overlap of p - p orbitals (pi bonds - two)
- C-C bond length 1.20 Å
- C-C bond strength 200 kcal/mole
- C-H bond length 1.06 Å
- C-H bond strength 125 kcal/mole
- orientation - linear
Bonding Trends
Bond Lengths in Angstroms (Bond Strengths in kcal/mole)
Compound Hybrid C-C bond C-H bond
Ethane sp3 1.54 (88) 1.10 (98)
Ethylene sp2 1.33 (152) 1.08 (103)
Acetylene sp 1.20 (200) 1.06 (125)
- multiple bonds are stronger
- shorter bonds are stronger
Electronegativity
- tendency of an atom to attract electrons in a covalent bond
- in the Periodic Table, electronegativity increases to the right and
up
- F > O > Cl ~ N > Br > C > H > metals
Polar Covalent Bonds
- electrons in a covalent bond may not be equally shared
H-Cl is actually d+ H-Cl d-
- where d+ or d- represents a partial charge
Polar Bonds to Carbon
- C-C bonds are nonpolar
- C-H bonds are generally considered nonpolar
- C-X bonds are polarized with carbon d+
for X = F, Cl, Br, I, O, S, N
- C-M bonds are polarized with carbon d-
for M = metals
Bronsted-Lowry Acid/Base
- acid - donates H+
- base - accepts H+
NH3 + H2O <==> NH4+ + OH-
base + acid <==> acid + base
- note conjugate acid-base pairs
(differ by H+)
Acidity Constant (Ka)
usually simplified to
HA <==> H+ + A-
Acid Strength (pKa)
- stronger acids have higher Ka
for HCl, Ka = 107
for CH3COOH, Ka = 10-5
(acetic acid, found in vinegar)
- pKa = - log Ka
- stronger acids have a lower pKa
for HCl, pKa = -7
for CH3COOH, pKa = 5
pH and pKa
- Ka = [H+][A-]/[HA]
- pKa = pH - log([A-]/[HA])
- for pH = pKa, [A- ] = [HA]
- for pH < pKa, HA predominates
- for pH > pKa, A- predominates
e.g., for acetic acid at pH = 7
[CH3COO-] > [CH3COOH]
Acid-Base Reactions
CH3COOH + OH- <==> CH3COO- + H2O
acid base base acid
pKa = 5 pKa = 15.7
stronger acid
reaction favored to the right
Acid-Base Reactions
CH3COOH + H2O <==> CH3COO- + H3O+
acid base base acid
pKa = 5 pKa = 1.7
reaction favored to the left
Acid-Base Reactions
HC=CH + Na+NH2- <==> HC=C-Na+ + NH3
acid base base acid
pKa = 25 pKa = 35
reaction favored to the right
Acid-Base Reactions
CH3OH + CN- <==> CH3O- + HCN
acid base base acid
pKa = 16 pKa = 9
reaction favored to the left
Lewis Acids
- acid - accepts an electron pair
- base - donates an electron pair
- (making a new covalent bond)
H+ + H2O <==> H3O+
L acid L base new O-H bond
BF3 + NH3 <==> F3B-NH3
L acid L base new B-N bond
Tues, Jan. 16
Formal Charge
- #valence e- - (# bonds + # lone e-)
- (How many e- is normal for this atom?)
- (How many e- in this compound?)
Resonance
- more than one possible Lewis structure for a compound
- What's the best Lewis structure?
- follow the octet rule
- electronegativity determines the best place to locate charges
carbon monoxide
nitromethane