![]()
![]()
![]()
1. (15 points) Write a complete IUPAC name for each of the following compounds, including designation of stereochemistry if it is specifically shown:
a) 
b) 
c) 
2. (10 points) Arrange the four isomeric butyl bromides (C4H9Br) in order of their expected reactivity in an SN2 reaction.

3. (15 points) Complete each of the following reactions by adding the missing part: either the starting compound, the necessary reagents and conditions, or the final major product. Indicate stereochemistry if it is specific.
a) 
b) 
c) 
d) 
e) ![]()
4. (15 points) Arrange the following in order with respect to the property indicated. Write "MOST" under the most reactive or highest value and "LEAST" under the least reactive or lowest value.
a) reactivity towards HNO3 / H2SO4

b) water solubility

c) nucleophilicity
![]()
d) acidity
![]()
e) cation stability
![]()
5. (15 points) Write a complete mechanism for the acid-catalyzed dehydration of 1-methylcyclohexanol. Show all steps.

What would be the name for the mechanism of this reaction?
Identify which step would be the rate-determining step.
There are two possible products formed (show both). Identify the major product. In which step is the product determined?
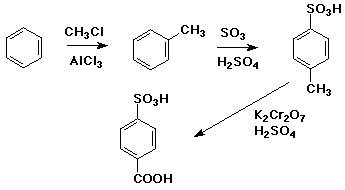
6. (15 points) Write a complete synthetic sequence to illustrate how you could prepare either one of the compounds below starting with benzene.
In your synthesis, show each reaction step with the necessary reagents and conditions, but it is not necessary to show reaction mechanisms.
CHOOSE JUST ONE


7. (15 points) Although a nitro group makes an aromatic ring much less reactive towards electrophilic substitution, a nitro group makes phenol a much stronger acid. Explain why these effects are opposite, specifically including resonance forms for the conjugate base of phenol.
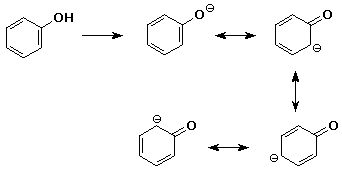
Predict whether m-nitrophenol or p-nitrophenol would be the stronger acid.