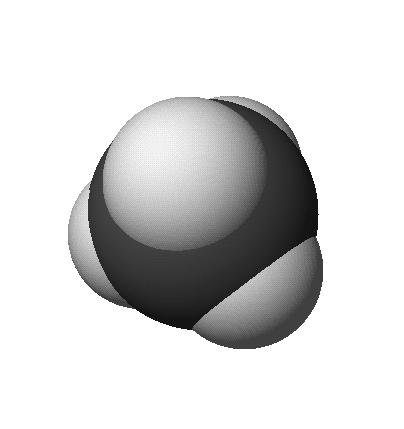Professor Carl C. Wamser
Professor Carl C. Wamser

Chapter 1 Notes - Bonding and Structure
organic chemistry
- carbon has unique chemistry
- bonds to every other element
- bonds to itself in long chains
- organic chemistry involves enormous variety
- many possible structures
- many possible reactions
organic chemists
- what do organic chemists do?
- understanding structures, reactions
- correlation of structures with properties
- synthesis of compounds with specific properties
- who else needs organic?
- basis of all life processes
- the great variety of structures and reactions make life possible
How to handle variety
- nomenclature - clear methods for naming structures and reactions
- structures - organized by functional groups
- reactions - organized by reaction types (what happens?)
- reactions - organized by reaction mechanisms (how does it happen?)
What should you get out of organic?
- from complex names, be able to derive a structure
- from complex structures, be able to identify functional groups, predict
characteristic properties
- work through reaction mechanisms - what is a molecule likely to do
under certain conditions
- "think like a molecule"
A reaction example
- CH3OH + HCl --> CH3Cl + H2O
- Reaction type ?
- acid/base, oxidation/reduction, addition/elimination, substitution,
rearrangement
- substitution - of Cl for OH (identify bonds broken and made)
- Reaction mechanism ?
- how does the reaction occur (step-by-step)
A reaction mechanism
- Break the molecules into atoms
- Reassemble into products
- What's wrong with this mechanism?
- It would take too much energy (unnecessarily)
A better mechanism
- Balance bond breaking with bond making
- First an acid-base reaction:
CH3OH + HCl --> CH3OH2+ + Cl-
- Then a substitution:
CH3OH2+ + Cl- --> CH3Cl + H2O
The Periodic Table
- atomic number (defines element)
- atomic weight (isotopes)
- electron shells (rows)
- groups (similar properties)
- filled shells (the noble gases)
- valence electrons (for bonding)
Lewis Structures
- the octet rule
- atoms strive to get 8 electrons (full shell)
- ionic bonding
- gaining or losing electrons
- stabilized by Coulombic attractions
- covalent bonding
- sharing electrons
- most common bonding in organic compounds
Atomic Orbitals
- wavefunctions
- describe location of electrons
- s orbital (spherical)
- p orbitals (three: x,y,z)
- (dumbbell shape - 2 lobes)
- d orbitals (4 lobes)
- not usually needed for organic chemistry
- hybrid orbitals
- combination orbitals
Hybrid Orbitals
- sp hybrids (one s plus one p)
- makes two identical orbitals (linear)
- sp2 hybrids (one s plus two p)
- makes three identical orbitals (trigonal)
- sp3 hybrids (one s plus three p)
- makes four identical orbitals (tetrahedral)
Bonding
- attraction between negative electrons and positive nuclei
- repulsions between electrons
- repulsions between nuclei
- bonding is a balance between the attractions and repulsions
- characteristic bond lengths and strengths
Molecular Orbitals
- overlap of atomic orbitals
- electrons are close to two nuclei
- bonding and antibonding combinations
Sigma Bonds
- cylindrical symmetry
- formed by end-on overlap
Pi Bonds
- nodal plane through bond axis
- formed by side-on overlap
Writing Organic Structures
- Lewis structures
- all electrons shown
- Kekule structures
- show bonds as lines
- lone pairs sometimes omitted
- line structures
- omit lone pairs
- omit hydrogens on carbons
- omit carbons
(assumed to be at the end of every bond)
3-Dimensional Structures
- dotted-line / wedge
- ball-and-stick
- space-filling
Visualizing chemical structures
- Name (common or systematic)
- Condensed Formula (as usually typed out)
- Lewis Structure (all atoms and bonds shown)
- Line Structure (omit hydrogens, assume carbons at vertices)
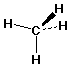
- 3-D Structure (show bond orientations)
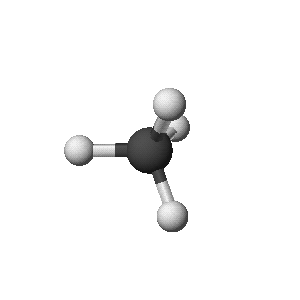
- Ball-and-Stick Structure (like a molecular model you could make)
- Space-Filling Model (approximates full size of electron distribution)
methane: CH4 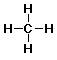
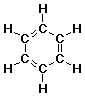
benzene: C6H6 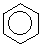
penicillin: 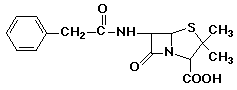
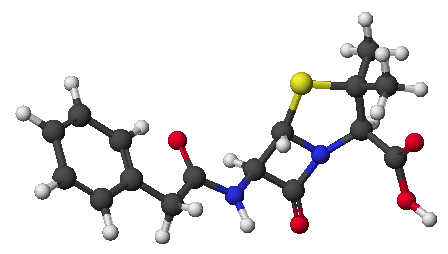
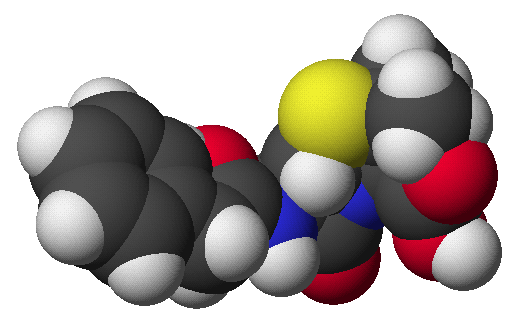
Try a 3-D image:
1) Click at the bottom after you read these instructions
2) Cross your eyes to see two double images
3) Make the middle images merge
Try it!
Typical Valence
- H 1 valence electron 1 bond
- C 4 valence electrons 4 bonds
- N 5 valence electrons 3 bonds + 1 lone pair
- O 6 valence electrons 2 bonds + 2 lone pairs
- F 7 valence electrons 1 bond + 3 lone pairs
Molecular Orbitals
- H + H ---> H-H
- s + s ---> sigma bond
- H-H bond length 0.74 Å
- H-H bond strength 104 kcal/mole
Methane
- C + 4 H ---> CH4
- sp3 + s ---> four sigma bonds
- C-H bond length 1.10 Å
- C-H bond strength 104 kcal/mole
- orientation - tetrahedral
- bond angles 109.5°
Why Hybrid Orbitals?
- good shape (directional)
- allows high overlap in bonding
- maximizes electron density between atoms
- good orientation
- minimizes repulsions between orbitals
Ethane
- CH3CH3
- includes a C-C sigma bond
- overlap of sp3 - sp3 orbitals
- C-C bond length 1.54 Å
- C-C bond strength 88 kcal/mole
- C-H bond length 1.10 Å
- C-H bond strength 98 kcal/mole
- orientation - two tetrahedra
Ethylene
- CH2=CH2
- includes a C=C double bond (alkene family)
- overlap of sp2 - sp2 orbitals (sigma bond)
- overlap of p - p orbitals (pi bond)
- C-C bond length 1.33 Å
- C-C bond strength 152 kcal/mole
- C-H bond length 1.08 Å
- C-H bond strength 103 kcal/mole
- orientation - planar
- bond angles 120°
Acetylene
- HCCH
- includes a CC triple bond (alkyne family)
- overlap of sp - sp orbitals (sigma bond)
- overlap of p - p orbitals (pi bonds - two)
- C-C bond length 1.20 Å
- C-C bond strength 200 kcal/mole
- C-H bond length 1.06 Å
- C-H bond strength 125 kcal/mole
- orientation - linear
Bonding Trends
Bond Lengths in Angstroms (Bond Strengths in kcal/mole)
Compound |
Hybrid |
C-C bond |
C-H bond |
ethane |
sp3 |
1.54 (88) |
1.10 (98) |
ethylene |
sp2 |
1.33 (152) |
1.08 (103) |
acetylene |
sp |
1.20 (200) |
1.06 (125) |
- multiple bonds are stronger
- shorter bonds are stronger
Identifying the Hybridization of Carbon
- identify sigma and pi bonds around the carbon atom
(you need one sigma bond for each neighboring atom
and you need a total of four bonds for carbon)
Neighboring Atoms |
Sigma Bonds |
Pi Bonds |
Hybrid |
Structure |
4 |
4 |
0 |
sp3 |
tetrahedral |
3 |
3 |
1 |
sp2 |
trigonal planar |
2 |
2 |
2 |
sp |
linear |
Electronegativity
- tendency of an atom to attract electrons in a covalent bond
- in the Periodic Table, electronegativity increases to the right and
up
- F > O > Cl ~ N > Br > C > H > metals
Polar Covalent Bonds
- electrons in a covalent bond may not be equally shared
H-Cl is actually d+ H-Cl d-
- where d+ or d- represents a partial charge
Polar Bonds to Carbon
- C-C bonds are nonpolar
- C-H bonds are generally considered nonpolar
- C-X bonds are polarized with carbon d+
for X = F, Cl, Br, I, O, S, N
- C-M bonds are polarized with carbon d-
for M = metals
Bronsted-Lowry Acid/Base
- acid - donates H+
- base - accepts H+
NH3 + H2O <==> NH4+ + OH-
base + acid <==> acid + base
- note conjugate acid-base pairs
(differ by H+)
Acidity Constant (Ka)
usually simplified to
HA <==> H+ + A-
Acid Strength (pKa)
- stronger acids have higher Ka
for HCl, Ka = 10E7
for CH3COOH, Ka = 10E-5
(acetic acid, found in vinegar)
- pKa = - log Ka
- stronger acids have a lower pKa
for HCl, pKa = -7
for CH3COOH, pKa = 5
pH and pKa
- Ka = [H+][A-]/[HA]
- pKa = pH - log([A-]/[HA])
- for pH = pKa, [A- ] = [HA]
- for pH < pKa, HA predominates
- for pH > pKa, A- predominates
e.g., for acetic acid at pH = 7
[CH3COO-] > [CH3COOH]
Acid-Base Reactions
CH3COOH + OH- <==> CH3COO- + H2O
acid (pKa = 5) + base <==> base + acid (pKa = 15.7)
reaction favored for stronger acid
reaction favored to the right
Acid-Base Reactions
CH3COOH + H2O <==> CH3COO- + H3O+
acid (pKa = 5) + base <==> base + acid (pKa = 1.7)
reaction favored to the left
Acid-Base Reactions
HC=CH + Na+NH2- <==> HC=C-Na+ + NH3
acid (pKa = 25) + base <==> base + acid (pKa = 35)
reaction favored to the right
Acid-Base Reactions
CH3OH + CN- <==> CH3O- + HCN
acid (pKa = 16) + base <==> base + acid (pKa = 9)
reaction favored to the left
Lewis Acids
- acid - accepts an electron pair
- base - donates an electron pair
- (making a new covalent bond)
H+ + H2O <==> H3O+
L acid + L base <==> new O-H bond
BF3 + NH3 <==> F3B-NH3
L acid + L base <==> new B-N bond
Formal Charge
- #valence e- - (# bonds + # lone e-)
- (How many e- is normal for this atom?)
- (How many e- in this compound?)
Resonance
- more than one possible Lewis structure for a compound
- What's the best Lewis structure?
- follow the octet rule
- electronegativity determines the best place to locate charges
carbon monoxide (CO)
nitromethane (CH3NO2)
![]()
![]()