
Chapter 26 - Metabolism

Metabolic Processes
- catabolism - breakdown of larger molecules to smaller
ones
- anabolism - buildup of larger molecules from smaller ones
Digestion
- a specific example of catabolism, in which food is broken
down to extract raw materials (for anabolism) and energy
- initial digestion steps are simple hydrolyses:
- fats -> glycerol and fatty acids
- carbohydrates -> glucose and other simple sugars
- proteins -> amino acids
- further digestion steps convert these molecules into acetyl
CoA, which enters the citric acid cycle and gets oxidized to
2 CO2
- the steps are oxidations and generate reduced cofactors
- the steps are exothermic and generate ATP for energy storage
- the net result of digestion is food -> CO2
plus reduced cofactors and ATP
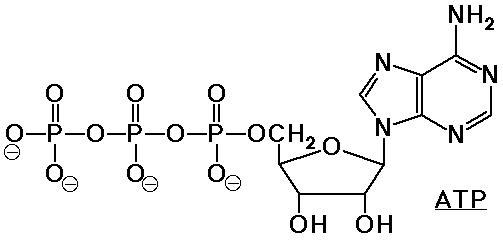
ADP / ATP
- ATP is used as stored energy, useful for coupling to other
reactions
- ATP hydrolysis to ADP plus phosphate releases 8 kcal/mole
- for example, glycerol -> glycerol phosphate is endothermic
but glycerol + ATP -> glycerol phosphate + ADP is exothermic
- ATP is coupled to many other reactions (not necessarily
involving phosphate) to make them more favorable
NAD+ / NADH
- NAD+ is used as a general oxidant
- reduction of NAD+ (by adding 2 e-
and H+) generates NADH
- NADH is used as a general reductant
- NAD+ and NADH are cofactors used with enzymes
that carry out oxidation or reduction reactions

FAD / FADH2 is another common reducing agent
Digestion of Fatty Acids - the Beta-Oxidation Pathway
- fatty acids are broken down 2 carbons at a time
- each stage releases one acetyl CoA and uses one FAD and
one NAD+ as oxidants
- oxidation creates a conjugated double bond (uses FAD)
- hydration of the double bond makes an alcohol
- oxidation of the alcohol makes a beta-keto ester (uses
NAD+)
- a reverse Claisen condensation gives acetyl CoA plus a
shorter CoA ester
- repeat steps 1 - 4 until the chain is broken down to only
two carbons (acetyl CoA)
Digestion of Glucose - Glycolysis
- breakdown of glucose in 10 steps to 3-carbon fragments,
eventually pyruvate
- uses 2 ATP to set up the breakdown, then gets back 2 ATP
from high-energy phosphates
- also uses 1 NAD+ as an oxidant
- glucose to glucose-6-phosphate (uses ATP)
- glucose-6-phosphate to fructose-6-phosphate
- fructose-6-phosphate to fructose-1,6-diphosphate (uses
ATP)
- reverse aldol reaction: fructose-1,6-diphosphate to dihydroxyacetonephosphate
+ glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
- dihydroxyacetonephosphate isomerized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
- glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate to glycerate-1,3-diphosphate
(uses NAD+)
- glycerate-1,3-diphosphate to 3-phosphoglycerate (generates
an ATP)
- 3-phosphoglycerate to 2-phosphoglycerate
- 2-phosphoglycerate to phosphoenolpyruvate
- phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate (generates an ATP)
Fates of Pyruvate
- anaerobic (regenerate NAD+, i.e., no net oxidation overall)
- reduction by NADH to lactate (generates an NAD+)
- decarboxylation to acetaldehyde, reduction to ethanol
(generates an NAD+)
- aerobic (use up more NAD+, i.e., overall oxidation)
- decarboxylation and coupling to CoA (uses NAD+)
- generates acetyl-S-CoA, which enters the Krebs cycle and
is oxidized to CO2
- the Krebs cycle generates additional ATP and NADH

