Chapter 2 - Alkanes. Nomenclature and Structure

Functional Groups
- a specific arrangement of atoms
- define chemical families
- determine chemical properties
- basis of nomenclature
- organization of textbooks
Hydrocarbons
- contain only C and H
- functional groups:
- only C-H and C-C single bonds (alkanes)
- C=C double bond (alkenes)
- CC triple bonds (alkynes)
- rings (cycloalkanes)
- aromatic rings (arenes)
- form basic carbon skeleton
Heteroatoms
- Halogens ( X = F, Cl, Br, I )
- Oxygen ( C-O , C=O )
- Nitrogen ( C-N , C=N , CN )
- Sulfur ( C-S , C=S )
- lots of other possibilities
- combinations of bonds
- other elements
Groups with Single Bonds
- R = general carbon group
- halides ( R-X )
- alcohols ( R-OH )
- ethers ( R-O-R )
- amines ( R-N )
- thiols ( R-SH )
- sulfides ( R-S-R )
Groups with Multiple Bonds
- carbonyl families ( C=O )
- imines ( C=N )
- nitriles ( CN )
Carbonyl Families
- carbonyls:
aldehydes ( R-CO-H )
ketones ( R-CO-R )
- carboxyls:
carboxylic acids ( R-CO-OH )
esters ( R-CO-OR )
amides ( R-CO-NHR )
Alkane Family
- methane CH4
- ethane CH3CH3
- propane CH3CH2CH3
- butane CH3CH2CH2CH3
- alkane CH3(CH2)nCH3
- CnH2n+2 (homologous series)
Higher Alkanes
- pentane C5H12
- hexane C6H14
- heptane C7H16
- octane C8H18
- nonane C9H20
- decane C10H22
- note the Greek prefixes
Alkane Isomers
- carbon skeletons
- straight-chain
- branched-chain
- cyclic chain
- constitutional isomers
- atoms connected in a different order
- butane and isobutane
- 3 pentane isomers
Butane isomers
n-butane 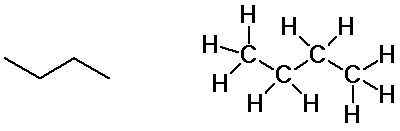
isobutane 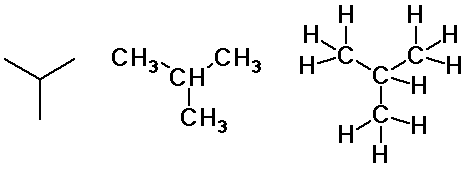
Pentane Isomers
- n-pentane
- isopentane
- neopentane
Alkyl Groups
n-propyl alcohol 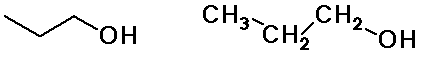
isopropyl alcohol 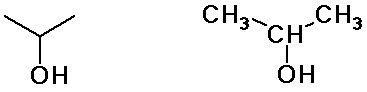
(constitutional isomers)
Butyl Groups
- n-butyl
- sec-butyl
- isobutyl
- tert-butyl
Classification of C Atoms
- 1° - primary - bonded to one other C
- 2° - secondary - bonded to 2 other C's
- 3° - tertiary - bonded to 3 other C's
- 4° - quaternary - bonded to 4 other C's
- class also applies to H atoms or functional groups attached to that
C
Identifying Carbon Classes
- identify the classes of each C, H and functional group in the molecule
below
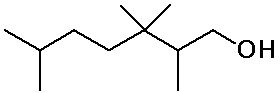
IUPAC Nomenclature
(prefixes)-(parent alkane)-(suffixes)
(substituents)-(longest chain)-(family)
Cl-CH2CH2-OH
2-chloro ethan ol
IUPAC Rules
- parent = longest continuous carbon chain
- number chain from end closest to a substituent (1st difference)
- assign numbers to each subst.
- in naming, arrange substituents alphabetically
- for multiple substituents, use prefixes di-, tri-, tetra-, etc.
- but they don't count when alphabetizing
- separate names from numbers with hyphens, numbers from numbers with
commas
- otherwise all written as one word
IUPAC Examples
- name the three isomers of pentane
pentane
2-methylbutane
2,2-dimethylpropane
IUPAC Examples
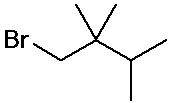
1-bromo-2,2,3-trimethylbutane
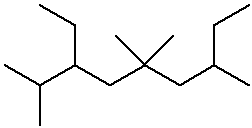
3-ethyl-2,5,5,7-tetramethylnonane
Writing Skeletal Structures
- omit C-H bonds
- assume C makes 4 bonds
- omit C atoms
- assume C at end of every bond
- especially useful for cyclic structures
- be able to put back all the details
Practice with Line Structures
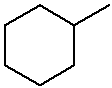 methylcyclohexane
methylcyclohexane
 tryptophane
tryptophane
molecular formula is: C11H12N2O2
Conformations
- different 3D structures of the same molecule, differing only by
rotations about single bonds
Ethane Conformations
C-H bonds on the two carbons may or may not align
eclipsed: C-H bonds are aligned 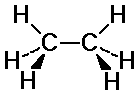
staggered: C-H bonds fit in between 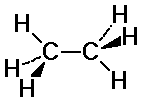
Newman Projections
- view down a C-C bond to visualize orientations
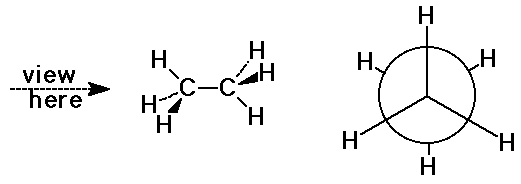
- staggered conformation (more stable)
Potential Energy Diagrams
- view energy changes as the C-C bond rotates
Thermodynamics / Equilibrium
for a general reaction:
A + B <==> C + D
equilibrium constant, K = [C] [D] / [A] [B]
favorable reactions have large K
unfavorable reactions have small K
Kinetics / rates of reaction
may or may not correlate with the favorability of the equilibrium
rate depends on the mechanism
what is the best way to get from reactants to products?
Heats of Reaction
delta H (enthalpy change)
delta H = H(products) - H(reactants)
exothermic means delta H < 0 (negative)
reaction gives off heat
endothermic means delta H > 0 (positive)
reaction absorbs heat
Potential Energy Diagrams
draw exothermic reactions downhill
draw endothermic reactions uphill
Activation Energy, Ea
there is usually an energy barrier between reactants and products
activation energy represents the highest amount of energy necessary
while travelling along the minimum-energy (easiest) pathway from reactants
to products
The Transition State
structure of the molecule(s) at the highest point along the reaction
pathway
the stability of the transition state (relative to reactants)
determines Ea (rate of reaction)

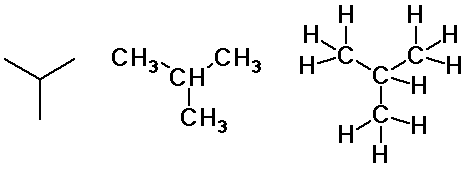
![]()
![]()
![]() methylcyclohexane
methylcyclohexane tryptophane
tryptophane![]()
