Organic Chemistry I
Dr. Carl C. Wamser
1. (15 points) Write a complete IUPAC name for each of the following compounds, including designation of stereochemistry if it is specifically shown:
a) 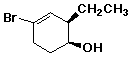
(1S,2R)-4-bromo-2-ethyl-3-cyclohexenol
b) 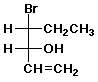
(3R,4R)-4-bromo-1-hexen-3-ol
c) 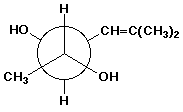
(2R,3S)-5-methyl-4-hexene-2,3-diol
2. (15 points) Identify the relationship between the two compounds in each pair below. Use the letters below to represent possible relationships:
A identical compounds
B conformational isomers
C constitutional isomers
D diastereomers
E enantiomers
F resonance forms
G other
a) 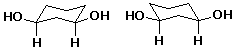 A
A
b)  F
F
c) 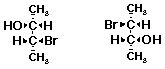 A
A
d) 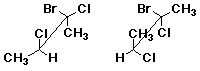 D
D
e) 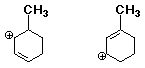 C
C
3. (10 points) Refer to the reaction below.
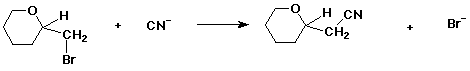
a) (3 pts) if the starting material is the S enantiomer, the product will be (circle one):
R / / S / / racemic / / can't tell / / other
b) (3 pts) if the starting material has (-) optical rotation, the product will necessarily be (circle one):
(+) / / (-) / / (+,-) / / can't tell / / other
c) (4 pts) Which of the following structures is the most stable conformation of trans-1,3-dichlorocyclohexane? (circle it)
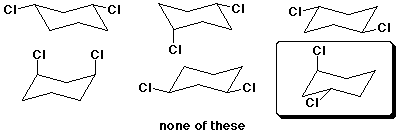
4. (20 points) Complete each of the following structures by adding the missing part. In each case the compound on the left is complete and the compound on the right needs to be completed to be equivalent to the structure on the left.
a) 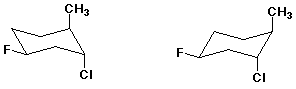
b) 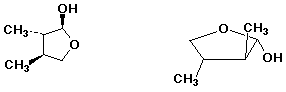
c) 
d) 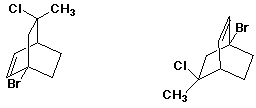
e) 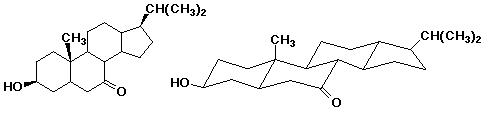
5. (15 points) Complete each of the following acid base reactions and identify the preferred direction of the equilibrium (right or left).
a) ![]()
b) 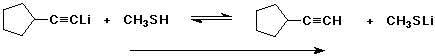
c) ![]()
d) Select the strongest base from among all the compounds used in the above equations (both sides).
6. (15 points) Arrange the following in order with respect to the property indicated. Write "MOST" under the most reactive or highest value and "LEAST" under the least reactive or lowest value.
a) nucleophilicity
![]()
MID / / MOST / / LEAST
b) basicity
![]()
LEAST / / MID / / MOST
c) acidity
![]()
MID / / MOST / / LEAST
d) rate of SN1 reaction
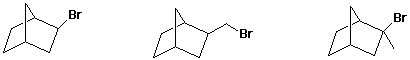
MID / / LEAST / / MOST
e) boiling point
![]()
MID / / MOST / / LEAST
7. (15 points) Complete each of the following reactions by adding the missing part: either the starting compound, the necessary reagents and conditions, or the final major product. Indicate stereochemistry if it is specific.
a) 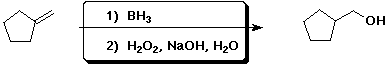
b) 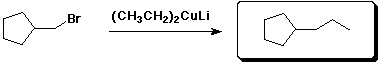
c) 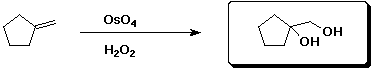
d) 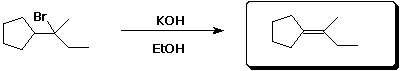
e) 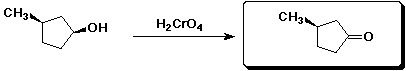
8. (20 points) Write a complete free radical chain mechanism for the bromination of cyclohexane, including all steps.
Also write a balanced equation and calculate DH for the overall reaction.

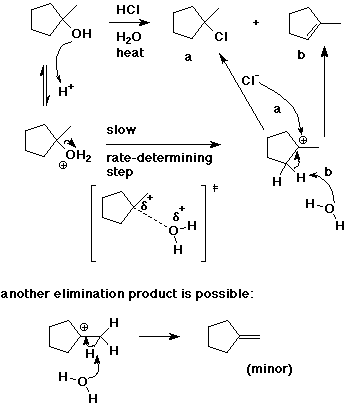
9. (20 points) Write a complete mechanism for the following reaction. Show all steps and all intermediates involved. Use electron-pushing arrows to indicate electron flow for each step.
Indicate the rate-determining step and write a transition state for it.
Predict at least one other minor product that should be expected.
10. (20 points) Use the table of bond dissociation energies to calculate H for each of the following reactions.
a) ![]()
DH = 93 + 38 - 107 - 136 = - 112 kcal/mole
b) ![]()
DH = 92 + 88 - 68 - 119 = - 7 kcal/mole
c) ![]()
DH = 88 + 104 - 100 - 105 = - 13 kcal/mole
d) Write a balanced reaction that shows the replacement of a 1° C-H bond with an OH group from water to make an alcohol (plus another product).
![]()
e) Calculate DH for your reaction d).
DH = 100 + 119 - 92 - 104 = + 23 kcal/mole
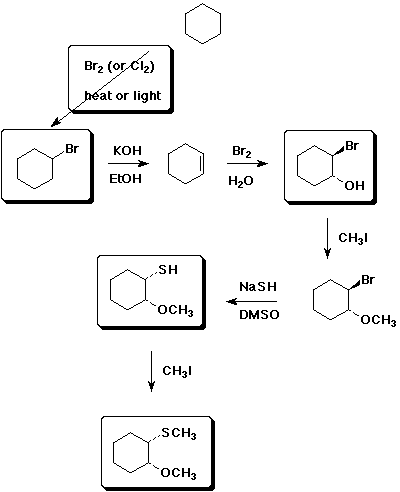
11. (15 points) Complete the following synthetic sequence by filling in the missing compounds or reagents in the empty boxes.
12. (20 points) You are attempting to determine whether the substitution reaction shown below proceeds by an SN1 or SN2 mechanism.
![]()
a) What product(s) would you predict if it followed an SN2 mechanism?
trans
b) What product(s) would you predict if it followed an SN1 mechanism?
both cis and trans
c) What conditions would you select to favor an SN2 mechanism?
polar aprotic solvent or phase-transfer catalysis, with CH3O- as strong nucleophile
d) What conditions would you select to favor an SN1 mechanism?
polar protic solvent to assist ionization, no strong bases or nucleophiles (outside of CH3OH)
e) If the actual experimental observation is that the product has a stereochemistry of 60 % trans and 40% cis, explain what you could conclude.
The reaction probably proceeded through an SN1 mechanism, although there could have been some SN2 as well.
Reasons for excess trans over cis could be:
- trans is more stable than cis;
- steric hindrance to cis attack of nucleophile by the CH3 group;
- steric hindrance to cis attack of nucleophile by the Br leaving group still nearby.