Organic Chemistry I
Dr. Carl C. Wamser
Listed below are the ConcepTests used in class, in the order they appeared. New questions and references to other related questions will be added as they become available. Boldface indicates the correct answer. Numbers indicate an estimate of your responses.
1. Where did you take General Chemistry?
A at PSU (100)
B at another Oregon college or university (50)
C at a college or university outside Oregon (20)
D never (0)
2. When did you take General Chemistry?
A this past summer (15)
B last year (120)
C 2-4 years ago (30)
D longer ago than 4 years (10)
3. Why are you taking organic chemistry?
A I'm a chem (or biochem) major (20)
B it's a requirement for a health professions program (140)
C it's a requirement for another program (10)
D it's a free elective (2)
4. Do you have an e-mail address, either at PSU or home?
A yes (170)
B no (6)
5. How many carbons are in tyrosine (shown below)?
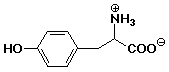
A 1
B 8
C 9 ( 98% )
D 10
6. How many hydrogens are in tyrosine (shown below)?

A 4 (5)
B 9 (2)
C 10 (10)
D 11 (150)
7. What type of reaction is
CH3OH + HCl -----> CH3Cl + H2O
A acid/base (150) X
B oxidation/reduction (0) (8)
C addition/elimination (2) (1)
D substitution (15) (160)
8. The only structure that does NOT have an error is D (98%)

9. The structure below that has an error is
A (6)
B (10)
C (20)
D (50)

10. Converting between the two resonance forms below
(left to right) involves electron pushing of
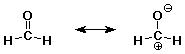
A a lone pair from O to C (0)
B a lone pair from C to O (50)
C a pi bond to C (10)
D a pi bond to O (50)
Which compound has the highest boiling point? C / B / B
Which compound has the lowest boiling point? A / A / C
11. ![]()
12. ![]()
13. ![]()
14. The amino acid glycine has two pKa values of 2.35 (carboxylic acid) and 9.78 (protonated amino group). At pH = 7 , glycine looks like: C

At pH < 2 , looks like B
At pH > 10 , looks like D
Note, texts will typically write amino acids as structure A, though this is never a major contributor at any pH.
15. How many stereocenters in morphine?

A 4
B 5
C 6
D more than 6
(Note that if N is considered a stereocenter, there are 6)
16. Is this structure (R) or (S) ?

A = R
B = S
17. Is this structure (R) or (S) ?

A = R
B = S
18. The stereochemistry is

A 1R,3R
B 1R,3S
C 1S,3S
D 1S,3R
19. Pure (S)-2-butanol has a specific rotation of +13.52°.
A sample of 2-butanol prepared
in the lab and purified by distillation has a calculated specific
rotation of +6.76°.
What can you conclude about the composition?
A 50% (S), 50% impurity
B 50% (S), 50% (R)
C 50% (S), 50% racemic
D some other mixture
20. How many stereoisomers? 2

21. How many stereoisomers? 4
![]()
22. Which ONE of the following structures is Z? D

23. Which of the following numberings is correct? D

24. Which compound is a possible product from addition of Br2 to 1-butene?
 D
D
25. Addition of Br2 to 1-butene would give 1,2-dibromobutane which is
A achiral
B racemic
C meso
D optically active
26. According to Markovnikov's Rule, addition of water to 1-butene should give a
A 1° alcohol
B 2° alcohol
C 3° alcohol
D none of the above
27. If a hypothetical reagent XY gave a syn addition to cyclopentene, the product would be
A cis
B trans
C a mixture of cis and trans
D neither cis nor trans
28. Addition of Br2 to cyclopentene would give a product which is
A achiral
B racemic
C meso
D optically active
29. Addition of Br2 to cis-2-butene would give a product which is
A achiral
B racemic
C meso
D optically active
30. Addition of Br2 to trans-2-butene would give a product which is
A achiral
B racemic
C meso
D optically active
31. Addition of OsO4 to cyclopentene would give a product which is
A achiral
B racemic
C meso
D optically active
32. Addition of BH3 followed by H2O2 to trans-2-butene would give a product which is
A achiral
B racemic
C meso
D optically active
33. Addition of BH3 followed by H2O2 to 1,2-dimethylcyclopentene would give a product which is
A achiral
B racemic
C meso
D optically active
34. Which will have the higher boiling point?
A CH3Br
B CH3CH3
35. Which will have the higher boiling point?
A CH3F
B CH3CH3
36. How many unique products are expected from monobromination of isobutane?
A 1
B 2
C 3
D more than 3
37. How many unique products are expected from monobromination of 2-methylbutane?
A 2
B 3
C 4
D more than 4
38. Using the table of bond dissociation energies, calculate DH for the reaction of cyclohexane with a chlorine atom:
A +3
B -3
C +7
D -7
39. Knowing DH for the above reaction, you can predict Ea for the reaction will be
A 0
B +7
C -7
D can't tell
40. Chemists actually determine Ea for a reaction by
A measuring product amounts
B measuring rates
C calculating from bond dissociation energies
D calculating from H values
41. How would the rate of the SN2 reaction between CH3Br and NaOCH3 be affected if the reaction mixture was diluted to twice the volume?
A twice the rate
B half the rate
C one-fourth the rate
D can't tell
42. How would the rate of the SN1 reaction between t-butyl bromide and NaOCH3 be affected if the reaction mixture was diluted to twice the volume?
A twice the rate
B half the rate
C one-fourth the rate
D no change
43. How would the rate of the SN1 reaction between t-butyl bromide and NaOCH3 be affected if more NaOCH3 was added to make twice its concentration?
A twice the rate
B half the rate
C four times the rate
D no change
44. Which of the following does NOT convert an alcohol into
a good leaving
group for a substitution reaction?
A PBr3
B HBr
C Na
D SOCl2
45. In the reaction shown below, the carbon bonded to Br was originally which carbon? C

46. In the reaction shown below, the six-membered ring is generated by shifting which bond? A

47. The pinacol rearrangement of cis-1,2-cyclohexanediol gives which product?
A cyclohexanol
B cyclohexene
C cyclohexanone
D none of the above
48. Periodic acid treatment of cis-1,2-cyclohexanediol gives which product?
A 1,2-cyclohexanedione
B hexanedial
C hexanedioic acid
D none of the above