Organic Chemistry I |
Final Exam Answer Key |
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
![]()
Organic Chemistry I |
Final Exam Answer Key |
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
![]()
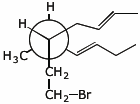
1. (25 points) Write complete names for each of the following.
a) ![]()
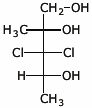
d) 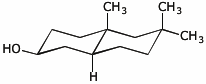
e) 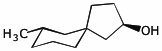
2. (15 points) Write accurate structures for the following:
a) a meso compound of formula C9H20
b) (1S,2R)-1-ethyl-2-methylcyclohexane in its most stable chair conformation
c) a trisubstituted alkene of formula C6H11Br with no stereochemistry possibilities (no R, S, E, or Z)
d) the enol formed from hydration of 3-hexyne
e) both enantiomers of 2-pentanol in Fischer projections (identify the R and S isomers)
3. (15 points) Arrange the following in order with respect to the property indicated. Write “MOST” under the compound with the highest value and “LEAST” under the compound with the lowest value.
a) basicity
b) heat of combustion
c) nucleophilicity
d) reactivity towards KCN in DMSO
e) ratio of substitution over elimination in reaction with KOH in ethanol
4. (15 points) Complete each of the following reactions by adding the missing part: either the original reactant, the necessary reagents and conditions, or the final major product.
Show stereochemistry if it is specific. If a product is racemic, indicate that.
a) 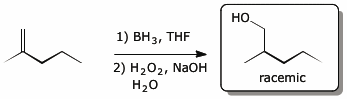
b) 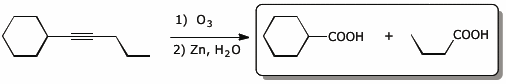
c) 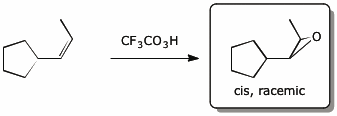
d) 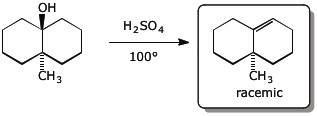
e) 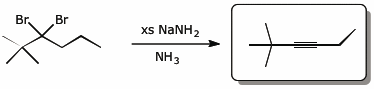
5. (15 points) Complete each of the following reactions by adding the missing part: either the original reactant, the necessary reagents and conditions, or the final major product.
Show stereochemistry if it is specific. If a product is racemic, indicate that.
a) 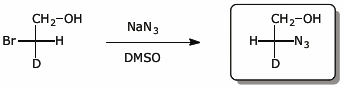
b) 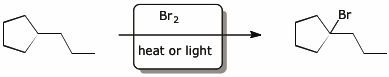
c) 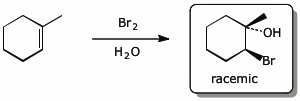
d) 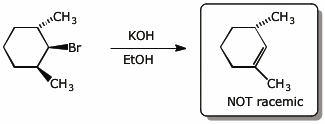
e) 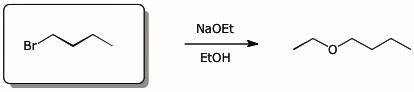
6. (15 points) Complete each of the following structures by adding the missing substituents on the right side so that the structure is equivalent to the complete structure on the left side.
a) 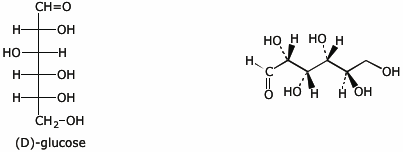
b) 
c) 
7. (15 points) Use the table of bond dissociation energies to calculate delta H for each of the following reactions. It’s only necessary to set up the calculation by showing the equation and the bond energies you would use for your calculations. Use units of kJ/mol.
a) 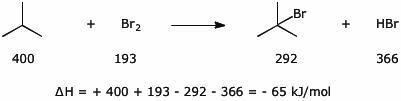
b) 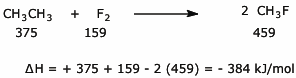
c) 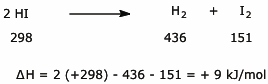
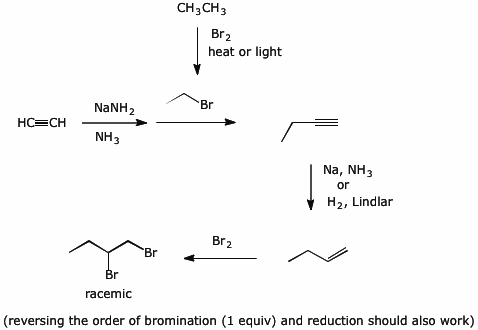
8. (20 points) Show a sequence of reactions that could be used to synthesize the following compounds. You may use acetylene and any alkane with three or fewer carbons as the only source of the carbons in your final product.
No mechanisms needed.
a) ![]()
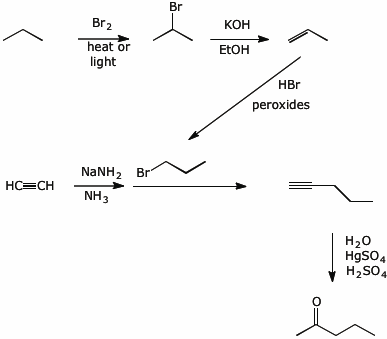
b) 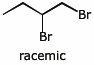
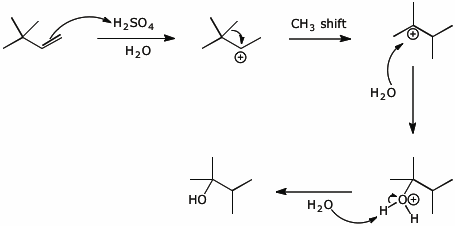
9. (15 points) Write a complete mechanism for the hydration reaction shown below. Show the pathway to the expected major product. Show all steps and show electron-pushing arrows in each step.
![]()
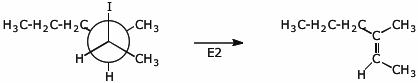
10. (15 points) Write a Newman projection for (2R,3R)-2-iodo-3-methylhexane, looking down the C2-C3 bond. Show the conformation that will allow an E2 elimination upon treatment with strong base. Predict the major product that would be expected upon E2 elimination, including specific stereochemistry.
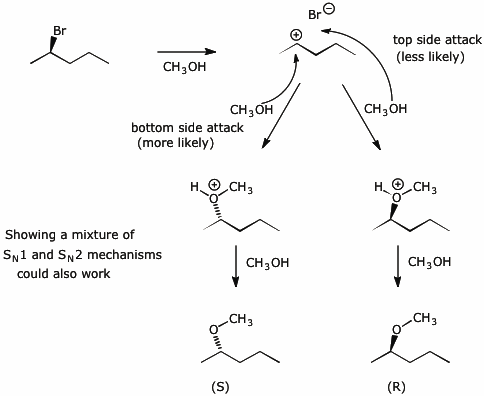
11. (15 points) The pure (R) enantiomer of 2-bromopentane has a specific rotation of -33°.
The pure (R) enantiomer of 2-methoxypentane has a specific rotation of +18°.
When optically pure (R)-2-bromopentane is allowed to warm in methanol, 2-methoxypentane is formed with a measured specific rotation of -6°.
What is the optical purity of the product?
6/18 = 1/3 = 33.3%
What is the enantiomeric excess of the product?
6/18 = 1/3 = 33.3%
What is the actual composition of the product in terms of % R and % S enantiomers?
66.7% (S) and 33.3% (R)
Write a mechanism that would explain these results.
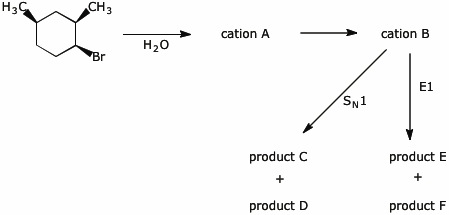
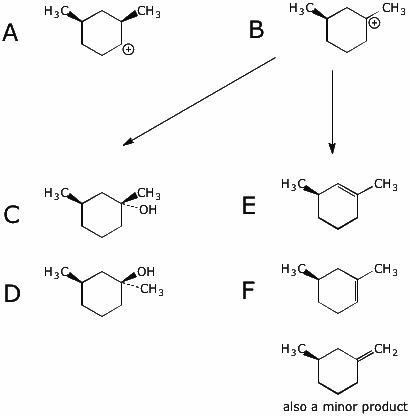
12. (20 points) Warming the compound below in the presence of water gives both SN1 and E1 products, as outlined in the scheme below. Write structures for each of the lettered compounds, paying particular attention to stereochemistry.
![]()