Organic Chemistry I |
Exam 1 |
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
![]()
Organic Chemistry I |
Exam 1 |
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
![]()
1. (15 points) Write complete names for each of the following.
a) 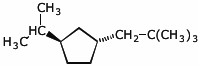
b) 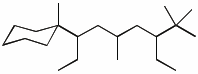
c) 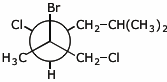
2. (15 points) Write accurate structures for the following:
a) a Newman diagram of gauche pentane
b) a compound of formula C5H12 with one tertiary carbon atom
c) 1-ethyl-5-methylspiro[2.4]heptane
d) the best chair conformation of trans-1,3-dimethylcyclohexane
e) the best Lewis structure for HCNO (bonded in that order)
3. (10 points) Complete the structures on the right so they are identical to the structures on the left.
The atom with the heavy dot should be the same one in both images.
a) 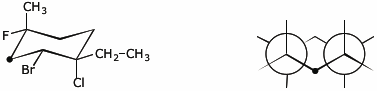
b) 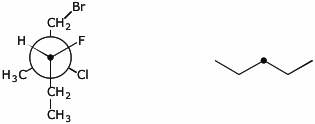
4. (15 points) Complete each of the following acid-base reactions. Identify the pKa values of the acids on each side of the equation and predict the preferred direction of the equilibrium.
a) ![]()
b) ![]()
c) ![]()
d) ![]()
Of all the compounds cited above (on both sides of the equations), which is the strongest acid?
Which is the strongest base?
Which equation will have the most balanced equilibrium constant (closest to [products] = [reactants])?
5. (15 points) Arrange the following in order with respect to the property indicated. Write MOST and LEAST under the compounds with the highest and lowest values of that property.
a) acidity
![]()
b) boiling point
![]()
c) stability
![]()
d) heat of combustion per mole
![]()
e) fraction of equatorial Cl at equilibrium
![]()
Place a methyl group at C3 on both conformations and predict which would be preferred.
7. (20 points) Write Newman diagrams in all three staggered conformations for 1,2-dibromobutane.
(HINT - first write the line structure so you start out right)
looking down the C1-C2 bond -
looking down the C2-C3 bond -
Assuming the relative group sizes are in the following order, predict the relative stabilities of each structure within each group of three conformations.
Br > CH2Br > CH2CH3 > CH3 > H
![]()