Organic Chemistry I |
Final Exam Answer Key |
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
![]()
Organic Chemistry I |
Final Exam Answer Key |
Professor Carl C. Wamser |
![]()
1. (25 points) Write complete names for each of the following.
a) 
b) 
c) 
d) 
e) 
2. (15 points) Write accurate structures for the following:
a) a Newman projection for the gauche conformer of pentane

b) the conjugate base of (R)-sec-butyl alcohol

c) the epoxide of cis-2-hexene
![]()
d) both propagation steps in the chlorination of methane

e) the rate equation for E2 reaction of t-BuBr with KOH/EtOH
![]()
3. (15 points) Arrange the following in order with respect to the property indicated. Write “MOST” under the compound with the highest value and “LEAST” under the compound with the lowest value.
a) heat of combustion
pentane 2-methylpentane 2,2-dimethylbutane
LEAST / / MOST / / MIDDLE
b) number of tertiary carbons
1-chloro-1-methylcyclohexane / 1-chloro-2,2-dimethylcyclohexane / 1-chloro-2,4-dimethylcyclohexane
MIDDLE / / LEAST / / MOST
c) nucleophilicity
KOH KOtBu KSH
MIDDLE / / LEAST / / MOST
d) boiling point
CH3OH CH3Br CH3F
MOST / / MIDDLE / / LEAST
e) reactivity with Cl2
methylcyclohexane 1-methylcyclohexene 1,1-dimethylcyclohexane
MIDDLE / / MOST / / LEAST
4. (15 points) Complete each of the following reactions by adding the missing part: either the original reactant, the necessary reagents and conditions, or the final major product.
a) 
b) 
c) 
d) 
e) 
5. (15 points) Complete each of the following reactions by adding the missing part: either the original reactant, the necessary reagents and conditions, or the final major product.
a) 
b) 
c) 
d) 
e) 
6. (15 points) Complete each of the following structures by adding the missing substituents on the right side so that the structure is equivalent to the complete structure on the left side.
a) 
b) 
c) 
7. (15 points) Use the table of bond dissociation energies to calculate (delta)H for each of the following reactions.
Show the bond energies you use for your calculations. Use kcal/mol.
a) 
b) 
c) 
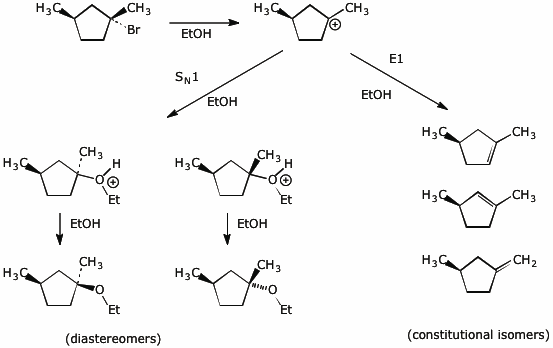
8. (20 points) (R,R)-1-bromo-1,3-dimethylcyclopentane undergoes both SN1 solvolysis and E1 elimination upon heating in ethanol.
Solvolysis gives two diastereomeric products and elimination gives three constitutional isomers.
Write a complete mechanism that shows all the steps leading to all of these products, specifically showing the stereochemistry at each step.
Electron-pushing arrows are optional.
9. (15 points) Show a sequence of reactions that could be used to synthesize the following compounds.
You may use acetylene and any alkane with four or fewer carbons as the only source of the carbons in your final product.
No mechanisms needed.
a) ![]()

b) ![]()

c) ![]()

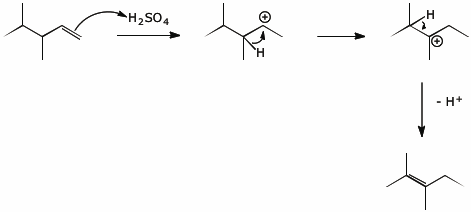
10. (15 points) In the presence of acid such as H2SO4, 3,4-dimethyl-1-pentene undergoes isomerization to 2,3-dimethyl-2-pentene.
Write a complete mechanism, showing all steps and using electron-pushing arrows.
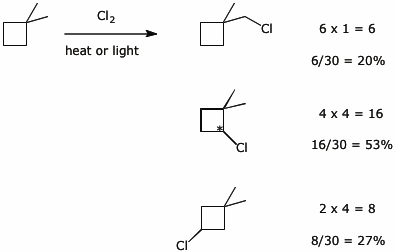
11. (15 points) Predict the products that would result from free radical monochlorination of
1,1-dimethylcyclobutane.
Predict the expected ratio of the different products, assuming the selectivity of Cl for C-H bonds is on the order 3° > 2° > 1° in the ratio 5 : 4 : 1 .
On the structures of the products, put * at every chirality center.
12. (20 points) Write Newman projections for the three staggered conformations of
(R)-2-bromobutane, looking down the C2-C3 bond.
Predict which of these conformations could lead to E2 elimination with a strong base, including the specific products formed from each conformation.
Which would you expect to be the major E2 elimination product and why?

![]()