The Systems View of a Sustainability
1. Simple steady state system, don't take out any more than you put in.
systems diagram
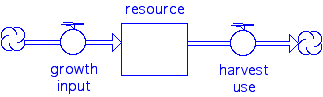
2. Strong and weak definitions of sustainability (ref ***)
weak, permissive, any form of capital can substitute for any other
strong, more limiting, natural capital can't be substituted
3. Sustainable natural capital
systems diagram
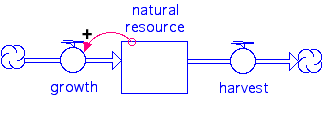
4.. Impact of use and the degradation from use
example systems diagram
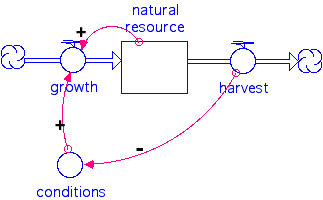
5. Effect of variation in conditions
example of diagram
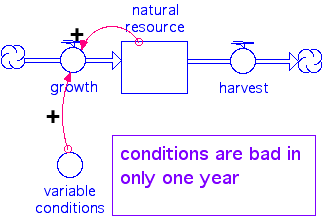
effect of one bad year (only 50% output) and an underestimate of true
maximum yield by only 5%
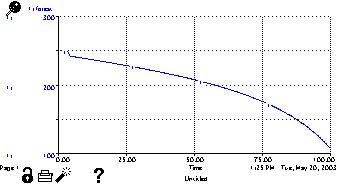
in 100 years you're down to less than 1/3 of your starting natural
capital
this means you not only have to have increased production (or decreased
harvest) in the good years
6. Summary of natural capital and sustainability
this systems view indicates that there are at least three ways to destroy
sustainability of your natural capital
a. simple overharvest, but this may be because you didn't have good
estimates for the maximum yield\
b. indirect effects from either harvest or use
c. risk of being too close to the maximum yield, one bad year and
the resource declines
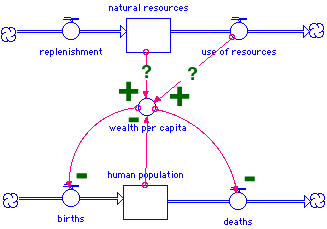
7. What is wealth
sustainability is maintaining capital for future generations to exploit
this is related to the concept of wealth
what does it mean to be wealthy
Is wealth the ability to spend resources or is it the amount of resources
that you have under your control?
|
![]()