15 October 2004
exam on next Friday, at least 3 exams
three gene test cross and tetrad analysis not included
Funny genetics story and excellent site dealing with dosage compensation
- thanks ML !!!!!
Chapter 5 Genetic mapping in eukaryotes
We will not cover the three point test cross or tetrad analysis
This chapter deals with gene linkage and gene mapping.
The first map was constructed by A. H. Sturtevant while a senior at Columbia
University and the favorite student of T. H. Morgan, using
the mutations white eye and yellow body.
Reference: Weiner, J. 1999. Time, Love, Memory : A Great Biologist and
His Quest for the Origins of Behavior. Knopf New York.
Example of Gene map, Human Genome Project ... Chromosome22.gif
Most important item: learn about parental and recombinant gametes and
and parental and recombinant progeny
P-generation; the parents and their parental gametes
ParentalRecombGametes1.GIF
The F-1 and its gametes; which are parental and which are non parental?
We will call the non parental gametes ----- recombinant gametes
ParentalRecombGametes2.GIF
What is the frequency of recombinant gametes?
ParentalRecombGametes3.GIF
Wow! this is independent assortment
ParentalRecombGametes4.gif
It is best to use a test cross in recombination mapping; why?
identify parental and recombinant
progeny in F-2 ? Dihybrid.gif
identify parental and recombinant progeny in test cross ?
Why use a test cross?
The test cross is: a heterozygous individual with one homozygous
recessive for the gene or genes in question
like: Ss Yy x ss yy
there is a heterozygous parent and a homozygous recessive parent
In a test cross there is only one genotype for each phenotype;
so by looking at the phenotype we may predict the genotype
of the gamete from the heterozygote.
In the F-2, with one exception, each phenotype is represented
by more than one genotype
Determination of recombination distance between two genes
Black body and vestigial wing are recessive mutations ...
Test cross allows for prediction of gametes
Test cross data for black and vestigial
The cross
put in genotypes/sperm
predict egg genotypes
conclusion: genes are on the same chromosome
what is going on?
from meiosis part of the course
conclusions for our two gene example
The recombination frequency in this cross is 17%
by convention, we say that black and vestigial are 17 map units
apart
one percent recombination frequency = one map unit
1 map unit = 1 centi Morgan (cM)
For a two gene test cross 50% is maximum recombination frequency
one cross over in one cell:
one cross over in all cells:
one cross over in some cells:
Cross over in no cells
The maximum RF in a two gene test cross is 50%
A RF of 50% is independent assortment; the genes may be on
the same chromosome or on different chromosomes.
A RF of less than 50% indicates that the genes are on the same
chromosome.
Recombination between genes results from:
the genes being on different chromosomes (inter-chromosomal)
the genes being on the same chromosomes (intra-chromosomal)
***** Random alignment of bivalents in metaphase-I gives inter-chromosomal
recomb
***** Crossing over in pachytene gives intra-chromosomal recombination.
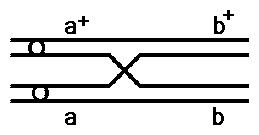
In general, the number of cross over events relates to the distance
between the genes.
Genes close together on a chromosome will have a low frequency
of crossing over
Genes far apart will have a high frequency of crossing over.
Multiple crossover events between two genes will result in an error
in calculating map distances.
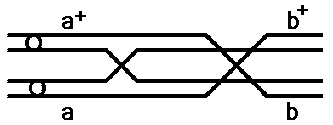
Two crossovers in all cells
Again, the maximum recombination frequency in a two gene test cross
is 50%
Turns out that frequencies of 10% or lower are accurate; but beyond
10% the observed recombination frequency is an underestimate
of the real frequency.
Why? Within about 10% there will be only single crossover events;
beyond 10% there will be multiple crossovers
18 October 2004
reminder: Exam on Friday, through chapter 5. Chapter 21 not
included.
And, to finish up chapter 5 ...
Add a third gene cinnabar...
fit the gene into the map
Concept of linkage groups
As recombination data for a species accumulate genes appear to fall
into distinct groups, called linkage groups.
When a large number of genes are mapped the number of linkage groups
equals the haploid chromosome number. Surprised at this?
In corn, there are 10 linkage groups and the haploid chromosome
number is 10.
Problem of cis/trans (coupling and repulsion in text)
Difference between cis and trans..... CisTrans.GIF
Problem of long distances
Since the maximum recombination frequency for a two
gene cross is 50%, how do we establish distances for genes
located a great distance apart?
We add up the short distances of intermediate genes.
There are several formulae which compensate for long distances.
Here are data from one of these:
Observed RF Real map units (Kosambi)
10
10.1
30
34.7
40
55.0
Using the recombination map to predict progeny
Flash sequence ...../MaptoDataSequence2.html
Examples of genetics maps
reference: .....R.C.King, ed. Handbook of
Genetics Vol 2
Also, portion of Drosophila map on practice exam
and workbook p.31
Complete linkage in male Drosophila
melanogaster
In humans recombination frequency less in males than in females
early mapping in humans- X-linkage (considered on first exam)
grandfather method in humans; for certain X chromosome markers for
only some pedigrees, not in text
the method:
to determine if a woman is cis or trans
early mapping in humans- autosomal
Donahue, R. P., W. B. Bias, and J. H. Renwick. 1968 Probable assignment
of the Duffy blood group locus to chromosome 1 in man. PNAS
61: 949-955.
Association with the Duffy blood group with a chromosomal marker
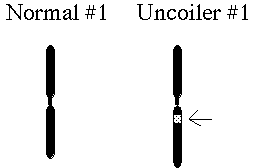
Magenis, R. E., F. Hecht, and E. W. Lovrien. 1970 Heritable fragile
site on chromosome 16: probable localization of haptoglobin
locus in man. Science 170.
Recombination mapping
Why recombination mapping? A way to organize genes, to learn the
biology of recombination, of value for medical counseling.
use of visible markers, like eye color and seed color, in many organisms.
Now use of DNA markers.
Example of Gene map, Human Genome Project ... Chromosome22.gif
Physical mapping
Discusssion in text of physical maps. These are maps which show
locations on chromosomes rather than locations via recombination frequencies.
deletion mapping in Drosophila shows band location of genes, example:
DrosMap.gif
